Deep Brain Stimulation Devices; Often Used To Treat Various Neurological Disorders
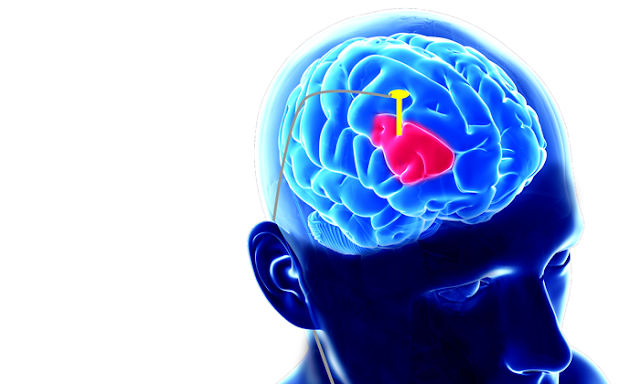
Deep brain stimulation devices are used to treat Parkinson’s disease. Deep brain stimulation (DBS) is a neurosurgical procedure used to place DBS devices, such as neurostimulator, which sends electrical impulses, through implanted electrodes, to treat movement disorders associated with Parkinson's disease, dystonia, essential tremor, and other neurological conditions. In short, DBS is a surgery done to implant deep brain stimulation devices that sends electrical signals to brain regions responsible for body movement. Electrodes are placed deep in the brain and are connected to a stimulator device. DBS devices do not cure the disease, they help reduce signs and symptoms. In some cases, medications may still be needed for certain conditions.
Deep brain stimulation devices are widely used to treat Parkinson's disease. The goal is to treat a patient's symptoms and improve their quality of life. Deep brain stimulation is a noninvasive surgical procedure that targets the brain with electrical pulses. During the procedure, wires from electrodes are placed under the patient's skin and guided down to a battery-operated pulse generator. A doctor will carefully monitor the patient during the procedure to ensure proper placement of the electrodes. The amount of stimulation is customized depending on the patient's condition and may take four to six months to reach its optimum setting.
The lead is a coated wire with electrodes at its tip. The electrodes deliver electric pulses to the brain tissue. The lead is placed inside the brain and connected to an extension wire through a small hole in the skull. The lead is attached to the neurostimulator with a small cable that runs from the scalp behind the ear to the neck or chest. The implanted stimulator can be used to treat movement disorders such as Tourette syndrome, OCD, and Parkinson's disease. The procedure requires an outpatient procedure. A surgeon attaches the frame to the patient's head with four pins. The patient is then stripped of hair and the skin is incised.


Comments
Post a Comment